The most work made on Evolutionary Developmental (evo devo) Biology
until recently was made on the known model organisms like Drosophila melanogaster, C. elegans, zebrafish and Xenopus laevis. However in the last couple of years much
information about evo devo was also made on plants to better understand plant
morphology and development patterns.
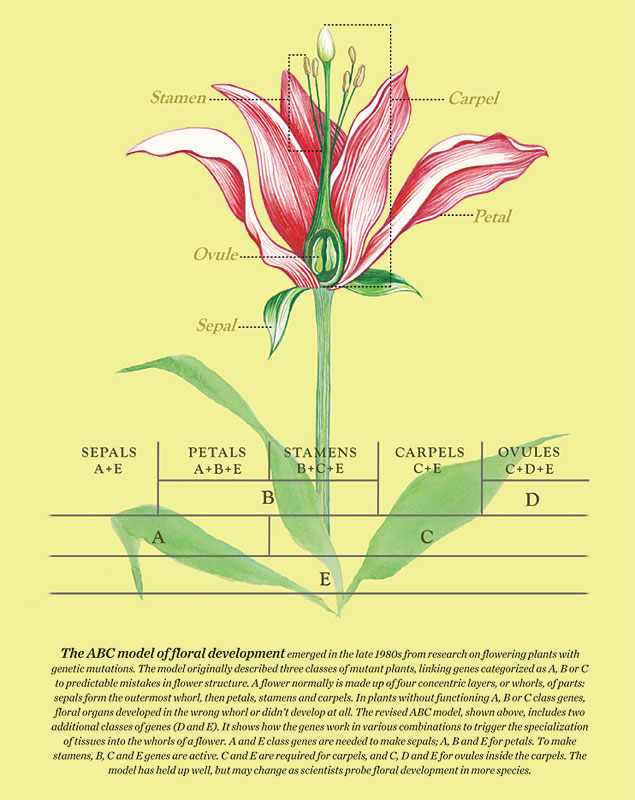
The ABC model is a system of floral development, established in the
1980. The model describes how the
structure of a flower emerges and which genes are involved in this
formation. A normal flower normally
consists of sepals, petals, stamens and carpels. For each of these organs exists specific
genes grouped in A, B or C class. Induced
genetic mutations helped establish this model in which different genes were
assigned to A, B or C classes, depending on their phenotypic change produced
after mutating a particular gene. In
this older model the A gens are involved in the production of the sepal, the A
and B genes for petals, the B and C genes for Stamens and the C gens for the
production of the carpels.
Fig. B: The ABCDE model system of floral development
The flower of the plants is one of the amazing innovations of nature to
diversify the angiosperms. Because of their
importance of flowering plants as a food source for humans it is important to
understand there evolution and development.
The floral structure is mainly constructed of four organ types, sepals,
petals, stamens and carpel. The
interesting fact is that these four structures can acquire a wide variety of
forms and changes. Some of these changes
can be the abortion of the organ, radial versus bilateral symmetry, dramatic
changes in the color patterns, changes in the number and size of the floral
organs or it can even develop new floral organs. Because of these interesting changes in the
flowering organs it is an interesting field for evo devo researchers to study
such interesting phenomenon. The results
gained on such plant organ changes will contribute significantly on the
understanding of morphology, developmental comparative studies and phylogenetic
analyses on model and non-model plants.
Plant Evolutionary Developmental (10 min)
(Plant Evolution (21min)
References:
J. L. Bowman, D. R. Smyth and E. M. Meyerowitz
(2012). The ABC model of flower development: then and now. Development 139,
4095-4098
The ABC model (2009), Building Beauty vol. 175, #8. D. E. Soltis ed al. (2007), The ABC Model and its Applicability to
The ABC model (2009), Building Beauty vol. 175, #8. D. E. Soltis ed al. (2007), The ABC Model and its Applicability to
Basal Angiosperms. Ann
Bot 100 (2): 155-163.

No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario